【THB】Failure Analysis

Recently, our technical engineers have carefully checked a defective bearing used in customers' food and beverage production line. There were records as to the bearing in terms of unstable application, damage, and failure.
In conjunction with the bearing examination and simulation with specific analysis software there are two findings below:
Finding 1:
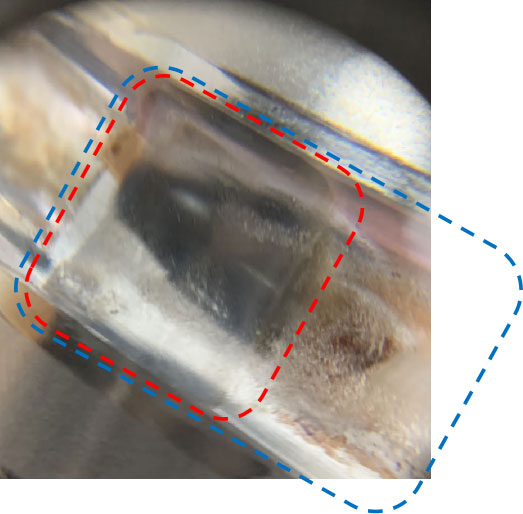
Fretting wear marks on the inner ring indicate a loose running fit between the inner ring and the shaft, which has been double checked from the analysis software-based load test results on the bearing under the specified duty.
This bearing is designed to operate under the point load. In case of a loose running fit, the inner ring tends to slide a little with continuous introduction of point loads, leading to unstable motion between the rolling body and the raceway, thus accelerating premature raceway wear.
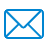
Finding 2:
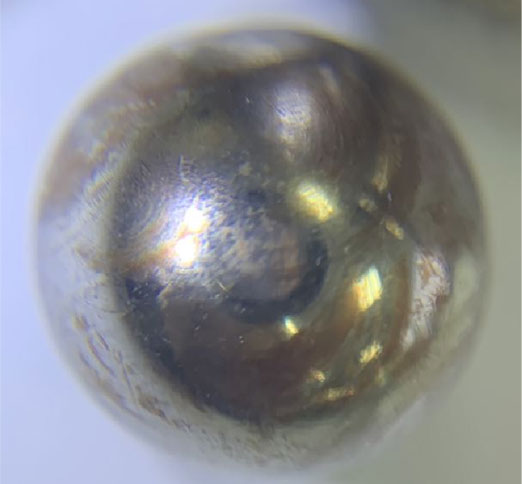
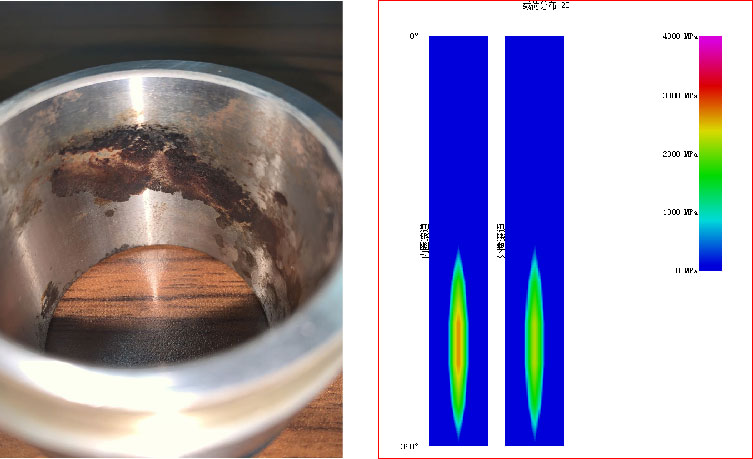
The "Cloud-style mark" is seen on the inner ring raceway and rolling body steel ball. The wearing of the ring raceway also indicates that the steel ball's motion in the raceway has really approached the shoulder, and wear marks of the raceway have nearly extended to cover the entire raceway width. It demonstrates the motion imbalance of the steel ball in the raceway.
Through software analysis of shaft deformation, the shaft deflection causes a certain deviation of bearing rotation from its axis so that the steel ball moves in a "S-shaped" or "Spectacle-shaped" pattern in the raceway. Furthermore, reciprocating motion at low loads was expected so that the steel ball had to repeatedly experience the process of start – acceleration – stop – restart – re-acceleration. This kind of reciprocating motion, coupled with the steel ball’s non-linear motion arising out of axis deviation, has caused the runout between the steel ball and the raceway as well as the oil shear, thus leading to the lubrication deterioration and premature wear.
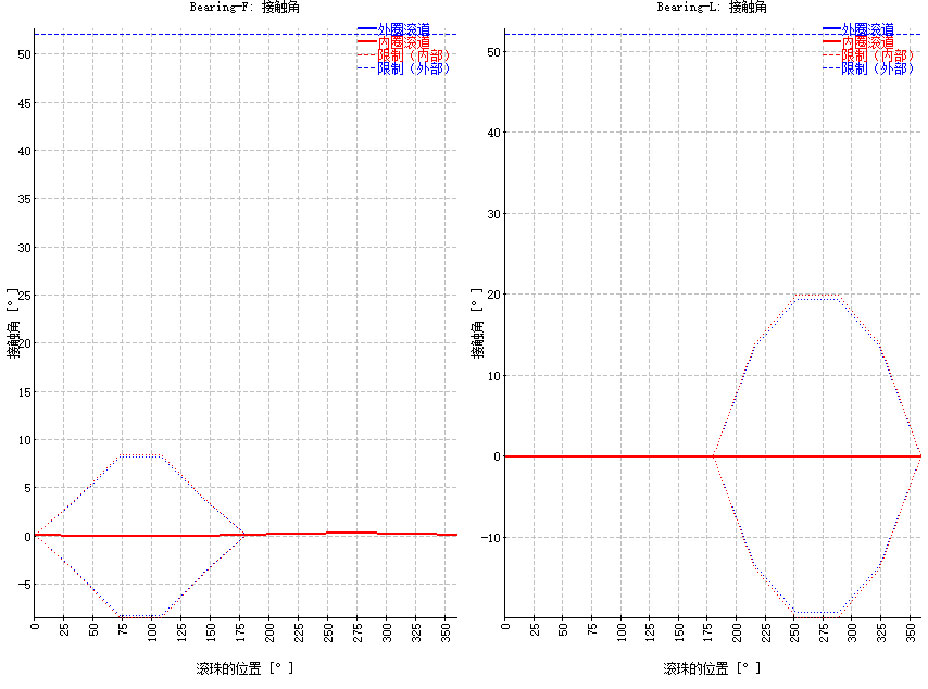
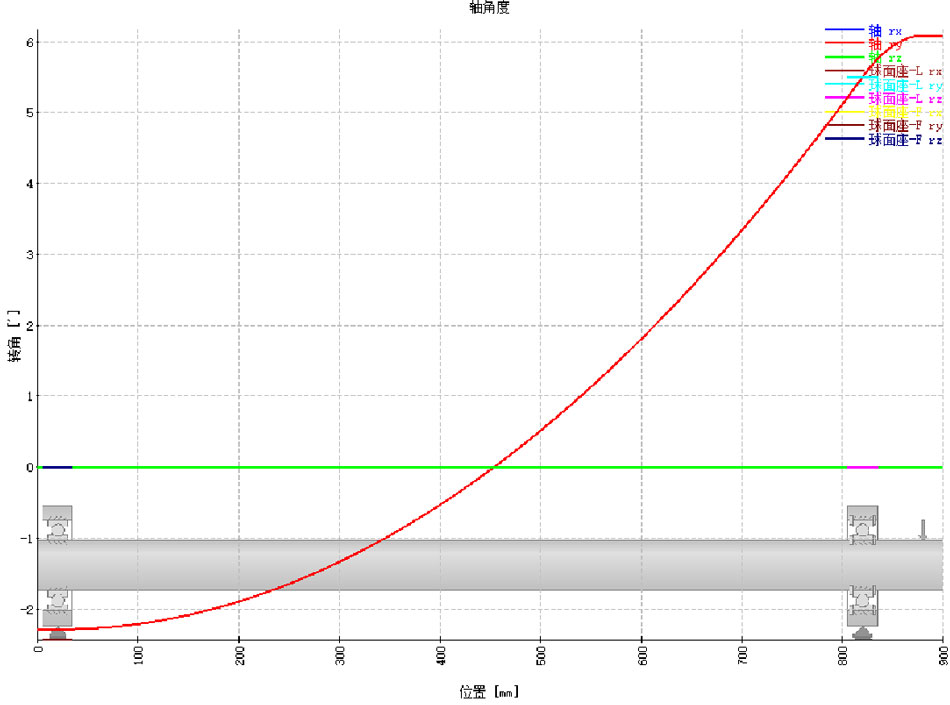
Given frequent occurrence of the foregoing factors in a period, raceway fatigue took place, thus eventually leading to bearing failure.
THB’s solutions are as follows:
1. Recommend use of an inner ring with adapter sleeve locking devices.
2. Optimize the shaft's fit with the inner ring (transition fit of j6)
3. The bearing’s inner ring groove shall be set with a groove curvature coefficient (fi=0.515) to enhance the contact area between the arc surface of the groove and the steel ball to reduce the tendency of steel ball rotation.
4. Use the C3 set or larger backlash (conducive to controlling the steel ball’s sideslip)
5. Use the grease containing solid additive or anti-wear additive.















 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  italiano
italiano 











 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  italiano
italiano