Key Technologies of Industrial Robot Bearings
Industrial robot bearings are one of the key supporting components of industrial robots, mainly including two types of bearings for industrial robots. One is thin-walled bearings with equal sections, and the other is cross-cylindrical roller bearings. In addition, there are also harmonic reducer bearings, linear bearings, joint bearings, etc., but the first two types of bearings are used more.
The development trend of modern industrial robots tends to be lightweight. Bearings must be installed in limited space, so they must be small in size and lightweight, that is, lightweight. However, at the same time, the high load-bearing capacity, high rotary precision, high operational stability, high positioning speed, high repeat positioning precision, long life, and high reliability performance of the robot require the matching robot bearings to have high load-bearing capacity, high precision, high rigidity, low friction torque, long life, and high reliability.
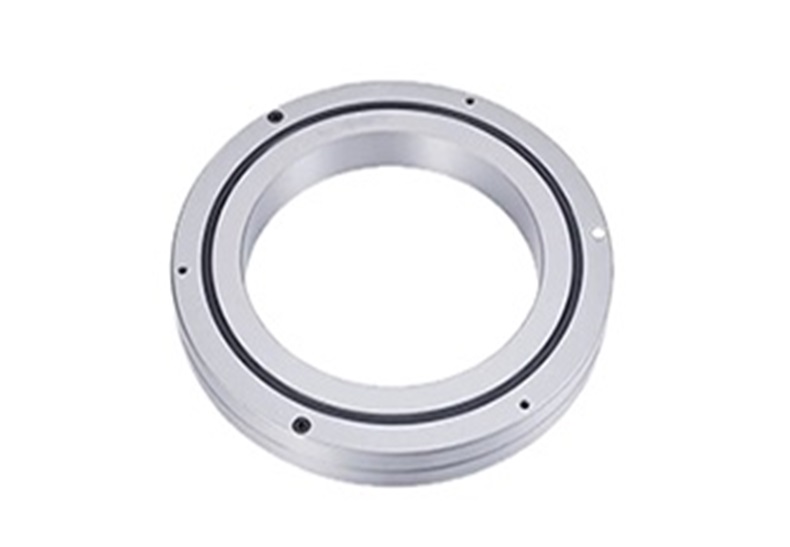
Thin-walled bearings with equal sections
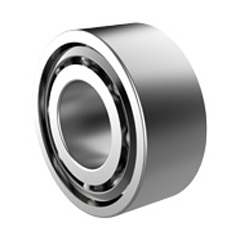
Thin-walled bearings with equal sections are different from ordinary thin-walled bearings. The cross-section of each series of equal sections is mostly square, and the size is designed as a fixed value. In the same series, the cross-sectional size does not change and remains constant regardless of the increase in inner diameter size. Therefore, it is called thin-walled bearings with equal sections. Thin-walled equal section ball bearings include thin-walled four-point contact ball bearings series, thin-walled angular contact ball bearings series, and thin-walled deep groove ball bearings. They are mostly used in areas of industrial robots such as the waist, elbow, and wrist that require small cross-sectional dimensions and restrictions. Under the same inner diameter size, thin-walled bearings with equal sections have more steel balls installed than standard rolling bearings, improving the internal force distribution of the bearing, reducing the elastic deformation at the contact between steel balls and grooves, and improving the load-bearing capacity of the bearing.
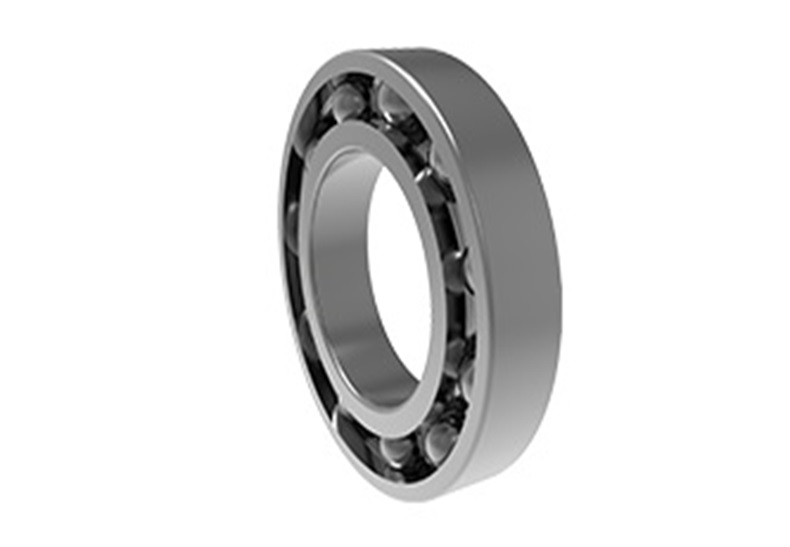
Thin-walled cross-cylindrical roller bearings
The internal structure of thin-wall cross cylindrical bearing adopts rollers arranged at 90° to each other. A single bearing can simultaneously withstand the joint action of radial force, bidirectional axial force and tilting moment. The rollers are equipped with spacer retainers or isolating blocks to prevent the inclination of the rollers or the mutual friction between the rollers, effectively preventing the increase of friction torque.
In addition, the structure of the rollers arranged perpendicular to each other can avoid the locking phenomenon of the rollers. At the same time, because the inner and outer rings of the bearing are segmented structures with adjustable clearances, even under pressure, it can still achieve high rotational accuracy. Thin-walled cross-cylindrical roller bearings are widely used in the waist rotation of industrial robots, articulated robots’ shoulders, arms, wrists, and other rotating parts due to their lightweight composite structure, high rotary precision, good rigidity, and stable friction torque.














 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  italiano
italiano 











 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  italiano
italiano