Comparison of Rolling Bearings and Plain Bearings
1. Introduction of plain bearings
Plain bearings, bearings that work under sliding friction. Plain bearings work stably, reliably and without noise. Under the condition of liquid lubrication, the sliding surfaces are separated by lubricating oil without direct contact, which can also greatly reduce friction loss and surface wear, and the oil film also has a certain ability to absorb vibration. But the starting friction resistance is large. The part of the shaft supported by the bearing is called the journal, and the part that matches the journal is called the bearing bush. In order to improve the friction properties of the bearing surface, the layer of anti-friction material cast on its inner surface is called a bearing lining. The materials of the bearing shell and bearing bush are collectively referred to as sliding bearing materials.
Commonly used sliding bearing materials are bearing alloys (also known as babbitt or white alloys), wear-resistant cast iron, copper-based and aluminum-based alloys, powder metallurgy materials, plastics, rubber, hardwood and carbon - graphite, polytetrafluoroethylene ( PTFE ). ), modified polyoxymethylene ( POM ), etc. Sliding bearing applications are generally under low speed and heavy load conditions, or operating parts where maintenance and lubricating oil are difficult.
2. Introduction of rolling bearings
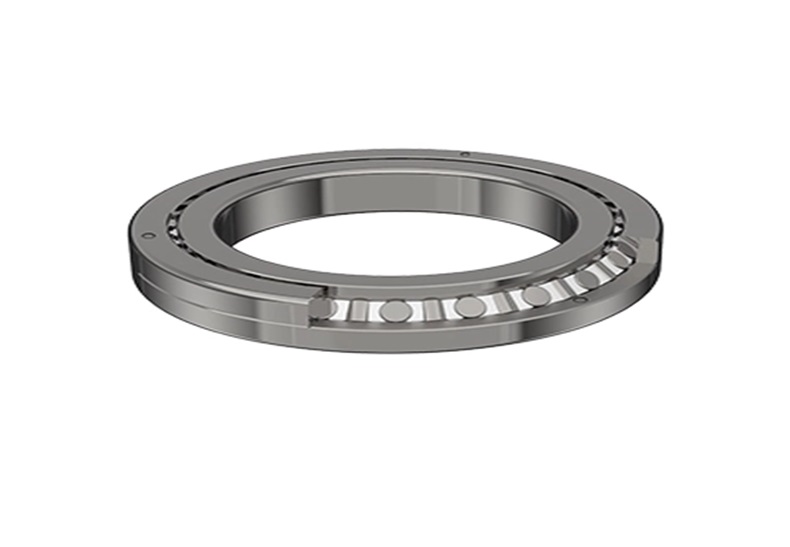
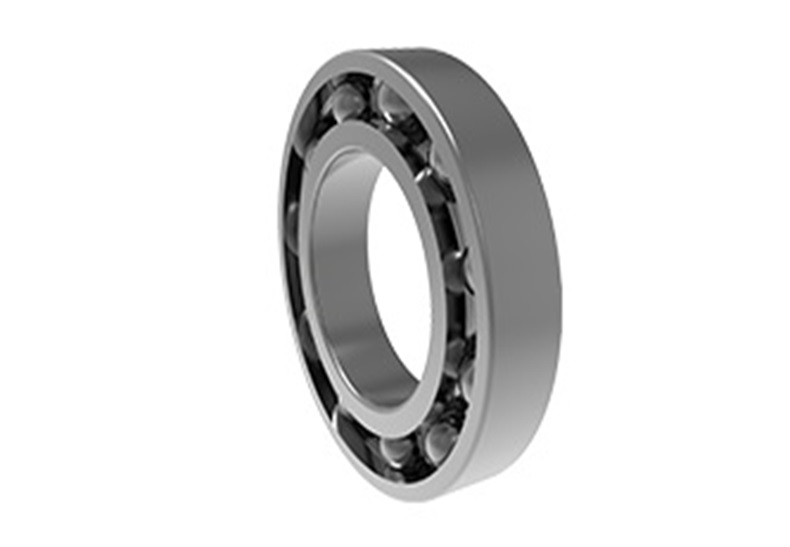
A precise mechanical element that reduces the friction loss by changing the sliding friction between the running shaft and the shaft seat into rolling friction is called a rolling bearing. Rolling bearings generally consist of an outer ring, an inner ring, rolling elements and a cage. The function of the inner ring is to cooperate with the shaft and rotate with the shaft, the function of the outer ring is to cooperate with the bearing seat and play a supporting role, and the rolling elements are evenly distributed between the inner ring and the outer ring by means of the cage. Its shape, size and quantity directly affect the performance and life of the rolling bearing. The cage can make the rolling elements evenly distributed, prevent the rolling elements from falling off, and guide the rolling elements to rotate for lubrication.
Rolling bearings are easy to use and maintain, work reliably, have good starting performance, and have high bearing capacity at moderate speeds. The radial bearing in the rolling bearing is usually composed of four parts: the inner ring, the outer ring, the rolling elements and the rolling element cage. The inner ring is tightly sleeved on the journal and rotates with the shaft, and the outer ring is installed in the bearing seat hole. There are raceways on the outer circumference of the inner ring and on the inner circumference of the outer ring. When the inner and outer rings rotate relative to each other, the rolling elements roll on the raceways of the inner and outer rings, and they are separated by the cage to avoid mutual friction. Thrust bearing is divided into two parts: tight ring and moving ring. The tight ring is tight with the shaft sleeve, and the moving ring is supported on the bearing seat. Rings and rolling elements are usually made of rolling bearing steel with high strength and good wear resistance, and the surface hardness after quenching reaches HRC60-65. The cage is mostly made of mild steel stamping, and can also be made of copper alloy cloth bakelite or plastic.














 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  italiano
italiano 











 English
English  français
français  Deutsch
Deutsch  italiano
italiano